IoT systems fail differently than traditional servers. Devices drop offline intermittently, data arrives late, firmware updates stall, and connectivity varies by location. When you treat IoT like standard infrastructure, problems surface too late.
This guide looks at IoT monitoring from a real operations perspective. It focuses on how devices behave in the field, what signals actually indicate trouble, and where common monitoring approaches fall short once hardware is involved.
You’ll learn what to monitor across devices, networks, and backends, how to spot failure patterns early, and how to keep distributed systems observable at scale. If IoT reliability matters to your product, this is where monitoring has to change.
Key takeaways:
- IoT monitoring is essential for ensuring security, performance, and efficiency across billions of connected devices—preventing downtime, failures, and breaches.
- Remote monitoring enables managing devices across vast geographies, while real-time alerts help detect issues instantly.
- Predictive maintenance powered by monitoring can reduce downtime by up to 45% and cut breakdowns by 70%.
- Top tools include UptimeRobot, AWS IoT Device Management, IBM Watson IoT, Datadog, and Microsoft Azure IoT Central, each offering scalability, integrations, and analytics.
- Use cases span industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, smart cities, and education—delivering improvements in uptime, efficiency, and safety.
- Challenges like data privacy, scalability, and legacy integration can be addressed with encryption, modular architecture, and middleware solutions.
- Future trends include AI-driven analytics, edge computing for faster decisions, and 5G-enabled real-time operations at scale.
- Best practices include setting clear KPIs, securing data, maintaining regular system updates, and investing in staff training for long-term success.
What is IoT monitoring?
IoT monitoring is the process of collecting, analyzing, and managing data from IoT devices and networks to maintain their security, performance, and efficiency. It provides real-time visibility, allowing businesses to detect issues, fix problems quickly, and optimize operations across connected devices. Think of it like a constant check-up for your devices, keeping everything running smoothly.
General vs remote IoT monitoring
General IoT monitoring refers to the process of collecting, analyzing, and managing data from IoT devices within a local network or confined area. This type of monitoring is often used in scenarios where devices are nearby and can be easily accessed.
Remote IoT monitoring, on the other hand, involves monitoring IoT devices and systems from a distance, often across different geographical locations. This approach is crucial for managing distributed IoT networks or devices in hard-to-reach areas.
Why is IoT monitoring critical in today’s interconnected world?
In 2025, 55.7 billion IoT devices generated 80 zettabytes of data2. Without proper monitoring, businesses risk losing access to this critical data, which is essential for informed decision-making and optimizing operations.
IoT monitoring also helps reduce downtime and prevent equipment failures. Organizations using predictive maintenance have achieved a 35-45% reduction in downtime3 and a 70% decrease in breakdowns.
Without proactive monitoring, companies expose themselves to heightened security threats. IoT-targeted cyberattacks increased by 400%4 in 2022, leading to greater operational inefficiencies.
Why is IoT monitoring important?
IoT monitoring keeps your networks running smoothly, securely, and reliably. With continuous performance tracking, you can stay ahead of potential issues, keeping your operations on track and uninterrupted.
Potential risks of not monitoring IoT networks:
- Security breaches: Without proper monitoring, IoT networks are vulnerable to cyberattacks. Hackers can exploit unsecured devices, leading to data breaches or system manipulation.
- System downtime: Unmonitored IoT systems are at higher risk of unexpected failures or performance degradation, leading to costly downtime and disruptions in services or operations.
- Data integrity issues: Lack of monitoring can lead to inconsistencies in data collection, which may result in incorrect analysis and flawed decision-making.
Benefits of IoT monitoring for businesses:
- Enhanced efficiency: Real-time monitoring keeps devices and systems functioning at their best, leading to more efficient operations and streamlined processes.
- Cost savings: Proactive monitoring helps identify issues before they escalate, minimizing the need for costly repairs or replacements. It also optimizes resource use, leading to lower operational costs.
- Predictive maintenance: By continuously monitoring IoT devices, businesses can detect early signs of wear or malfunction, allowing them to perform maintenance before a breakdown occurs, reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of equipment.
How does IoT monitoring work?
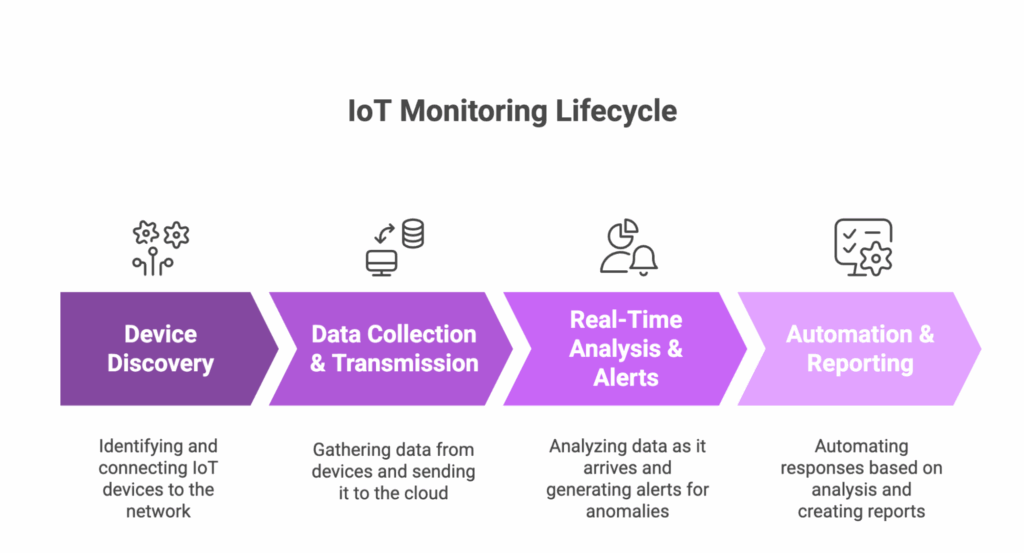
IoT monitoring operates through a structured process that focuses on maintaining the functionality, security, and performance of IoT devices and networks. Here’s how it works:
Step 1: Device discovery
The first step is identifying all IoT devices connected to the network. For example, in a smart factory, this could involve detecting all machines, sensors, and devices like temperature sensors, conveyor belts, and robotic arms.
The system scans the network, collects basic information like device names and IP addresses, and registers them in the monitoring system, so they can be tracked and managed..
Step 2: Data collection & transmission
IoT devices use embedded sensors to collect data and send it to a central system. For instance, in agriculture, soil moisture sensors placed in fields collect data on the soil’s moisture levels and send it to the cloud.
Step 3: Real-time analysis & alerts
Once data is collected, it’s analyzed in real-time to detect any issues. For example, in a smart building, energy usage data is constantly monitored. If the energy consumption exceeds a certain limit (say, when lights or HVAC systems are left on for too long), the system will send an alert to the facility manager to take action.
Step 4: Automation & reporting
Based on the monitored data, actions can be automatically triggered. For instance, in smart agriculture, if the soil moisture level falls below a certain point, the irrigation system automatically turns on to water the crops. Additionally, reports are generated for insights.
Key features of effective IoT monitoring systems
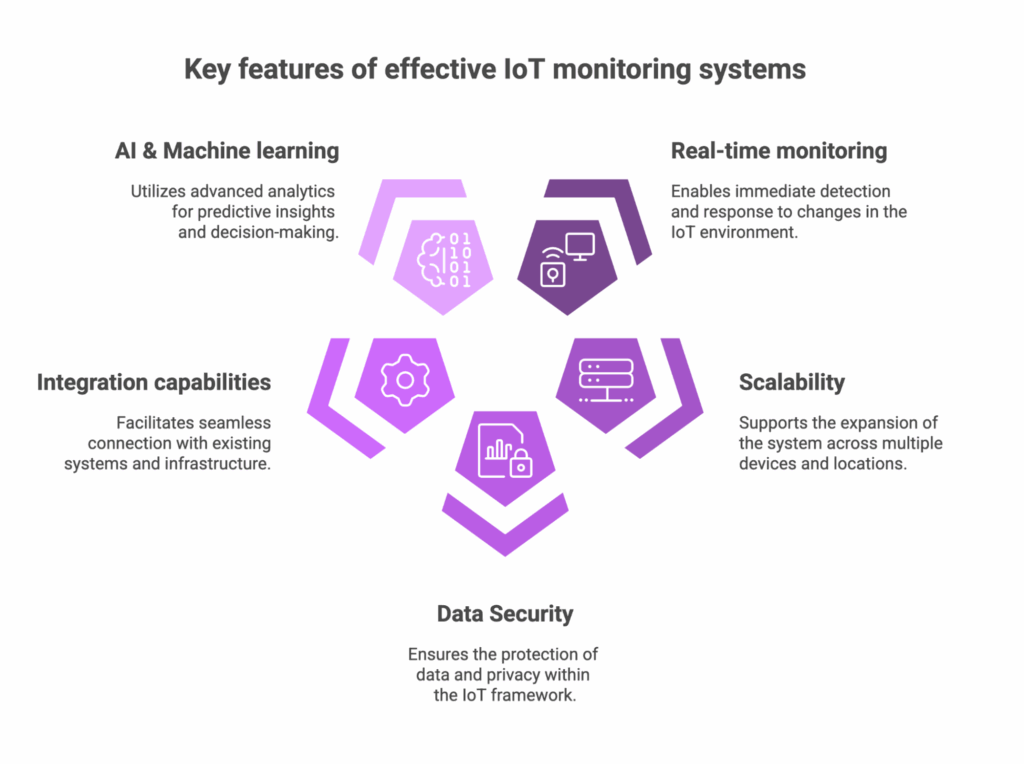
Effective IoT monitoring systems are designed to maintain the seamless operation, security, and performance of connected devices. The right features enable businesses to detect issues in real-time, optimize performance, and maintain the reliability of their IoT networks.
- Real-time monitoring and alerts
Real-time monitoring allows businesses to quickly detect and address issues as they happen. This helps prevent disruptions and downtime in critical operations.
UptimeRobot excels in providing continuous monitoring and instant alerts. Whether it’s device malfunctions or service downtimes, UptimeRobot ensures you’re notified immediately, helping your team stay ahead of potential problems. Additionally, its Public Status Pages feature allows businesses to share real-time operational statuses with stakeholders.
- Scalability across devices and locations
As IoT networks grow, scalability becomes essential. An effective monitoring system must adapt to handle a vast number of devices and locations, keeping operations smooth at any scale.
- Data security and privacy features
Security and privacy are crucial when dealing with IoT networks, as sensitive data is transmitted across devices. A strong monitoring system should protect this data and uphold compliance with privacy regulations.
- Integration capabilities with existing infrastructure
IoT monitoring should seamlessly integrate with existing business infrastructure for streamlined operations and insights.
UptimeRobot integrates with popular tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and others, enabling you to embed monitoring alerts and notifications directly into your workflow.
- Use of AI & Machine Learning for predictive analytics
Predictive analytics is an advanced feature that helps identify potential issues before they occur. By analyzing patterns and trends, businesses can take proactive steps to prevent costly downtime.
Top IoT monitoring tools and platforms (2026)
Here’s an in-depth look at the top 5 IoT monitoring tools and platforms in 2026 with a detailed description of each below the table.
| Tool | Key features | Pros | Cons | Use cases |
| UptimeRobot | – Real-time uptime monitoring- Supports 17+ integrations for instant notifications- Perfect for monitoring IoT device status | – Affordable pricing, including a free plan with 50 monitors.- Set up within 30 seconds- Instant alerts | – Primarily focuses on uptime, not full IoT management- Basic monitoring features | – Devices/Website uptime monitoring- API and server monitoring |
| AWS IoT Device Management | – Cloud-based IoT management- Device authentication- Data encryption- Integration with AWS | – Seamless integration with AWS services- Scalable- Secure management of devices | – Complex setup for new users- Cost can escalate with scale- Limited AI features | – IoT device management- Cloud-based IoT solutions |
| IBM Watson IoT | – AI-driven analytics- Predictive maintenance- Secure data handling- Device management | – Advanced AI and analytics- Highly secure- Scalable for large networks | – High cost- Complex setup and configuration- Requires deep technical expertise | – Predictive maintenance- Large-scale IoT networks |
| Datadog | – Full-stack observability- Anomaly detection- AI and machine learning analytics- Security monitoring | – Comprehensive monitoring across apps and infrastructure- Strong AI-powered insights- Integrates with cloud platforms | – Can be expensive- Requires technical expertise | – Full-stack infrastructure monitoring- Cloud app monitoring |
| Microsoft Azure IoT Central | – Integration with Azure IoT Hub- Real-time analytics- Secure device authentication- AI capabilities | – Seamless integration with the Microsoft ecosystem- Secure and scalable- Azure-based | – Requires Azure knowledge- Complex for small businesses- Pricing can be high | – IoT solutions in Azure environments- Industrial IoT systems |
UptimeRobot
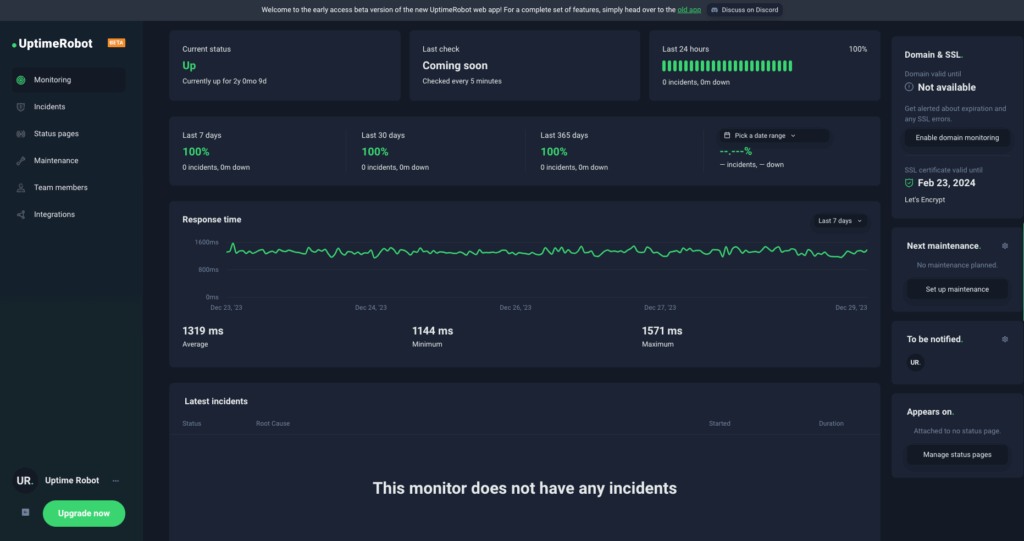
Uptime Robot is an uptime monitoring service. It tracks uptime and availability for websites, servers, ports, SSL certificates, domains, response time, and cron jobs. The platform performs periodic checks and sends real-time alerts when downtime is detected. It’s well-suited for businesses managing large-scale web services or IoT devices where consistent uptime and immediate troubleshooting are critical.
Features
- Real-time monitoring and alerts for IoT devices and services.
- Multi-location checks for accurate incident detection.
- Custom HTTP requests for advanced monitoring.
- Maintenance windows to pause monitoring during scheduled maintenance.
- Public status pages for sharing real-time operational status.
| Pros | Cons |
| Easy-to-use interface with customizable monitoring settings.Scalable, allowing businesses to monitor thousands of devices.Supports integration with popular platforms like Slack and Microsoft Teams.Provides detailed and instant alerts. | Limited support for some IoT-specific monitoring requirements.Designed primarily for website and service monitoring rather than specialized IoT monitoring. |
Keep an eye on your devices around the clock with UptimeRobot.
AWS IoT Device Management
AWS IoT Device Management is a cloud-based service that makes it easy to securely manage IoT devices throughout their lifecycle. It’s especially suited for industries like manufacturing and fleet management. Common use cases include remotely monitoring devices, organizing large fleets, and managing software and sensors across devices.
Features
- Bulk device registration for efficient onboarding.
- Query and aggregate device statistics based on attributes, state, and connectivity.
- Secure, bidirectional communication with remote devices for diagnostics and troubleshooting.
- Built-in support for ZigBee, Z-Wave, and Wi-Fi protocols for seamless device integration.
| Pros | Cons |
| Seamless integration with the AWS cloud ecosystem.Supports a wide range of IoT devices and industry use cases.Excellent SDK support for multiple programming languages. | Analytics and data visualization can be complex for new users.Pricing can be unpredictable, especially with large device deployments. |
IBM Watson IoT
IBM Watson IoT Platform is a cloud-hosted service on IBM Cloud. It helps businesses turn IoT device data into actionable insights using advanced analytics, machine learning, and cognitive computing. It’s ideal for large enterprises in manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare that need AI-driven monitoring, predictive maintenance, and operational optimization.
Features
- AI-powered platform for monitoring and managing IoT devices and data.
- Real-time insights and predictive maintenance using machine learning algorithms.
- Scalable platform designed to handle large IoT networks.
- Integration with enterprise systems, including ERP and CRM platforms.
- Security features for data encryption and secure device communication.
| Pros | Cons |
| Powerful AI and machine learning capabilities for predictive analytics.Smooth integration with IBM’s enterprise software ecosystem.Flexible deployment options across different environments.Efficient management of large-scale datasets for enterprise applications. | Pricing can be high for smaller businesses or limited deployments.Requires technical expertise to fully leverage the platform’s capabilities. |
Datadog
Datadog is a cloud-based monitoring and analytics platform. It is designed to provide real-time visibility into the performance of applications, infrastructure, and IT environments. It is well-suited for large enterprises that need deep insights into IoT systems and cloud infrastructure.
Features
- Real-time IoT monitoring and alerting.
- Comprehensive metrics and logs collection.
- Built-in security monitoring and analytics.
- Supports IoT device and service integrations.
| Pros | Cons |
| Powerful machine learning-based anomaly detection.Highly customizable dashboards for better visualization of IoT data.Seamless integration with cloud services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.Excellent for monitoring both IoT and cloud infrastructure. | Expensive pricing structure for smaller businesses.May require some technical expertise for advanced features. |
Microsoft Azure IoT Central
Microsoft Azure IoT Central is a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platform. It is developed to simplify the creation, deployment, and management of IoT solutions. Azure IoT Central is best for large-scale deployments that need a secure, scalable platform with predictive capabilities.
Features
- Cloud-based IoT monitoring platform with built-in security and compliance.
- Centralized device management for seamless reconfiguration and updates.
- Fast and secure connectivity between IoT devices and the cloud.
- Advanced data visualization and analytics for both high-level insights and granular details.
- Extensible architecture that integrates IoT data with business applications, enabling actionable insights.
| Pros | Cons |
| Highly scalable, making it suitable for large IoT networks.Deep integration with the Microsoft Azure ecosystem for a unified experience.Industry-specific templates tailored for sectors like retail, healthcare, government, and energy. | The pricing model lacks flexibility compared to some competitors.Limited customization options for businesses with highly specific needs. |
Industry-specific use cases of IoT monitoring
Key use cases of IoT monitoring include:
1. Manufacturing
Manufacturers rely on IoT to monitor equipment health, predict failures, and optimize maintenance schedules. By analyzing real-time sensor data, companies can reduce downtime, extend machine lifespan, and improve overall operational efficiency.
One example is Tenaris, a leading pipe manufacturer, which deployed IoT-based predictive maintenance in its Dalmine, Italy factory. Sensors on 290 low-voltage and 20 high-voltage motors detected anomalies in bearings, voltage, and power. The system identified a failing water pump early, enabling preemptive maintenance and ensuring uninterrupted operations.
Another example is GE, which leverages IoT sensors and AI for real-time equipment monitoring. This approach has led to a 25% reduction in unplanned engine removals in aviation, a 10% increase in power generation efficiency, and a 30% drop in manufacturing maintenance costs.
2. Healthcare
IoT enhances healthcare by enabling remote patient monitoring and smart medical devices that provide real-time health insights. These technologies improve patient care, reduce hospital visits, and allow faster responses to medical emergencies.
For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers developed an IoT-based health monitoring system with wearable sensors that tracked SpO2, heart rate, and temperature. The system transmitted data wirelessly to doctors, enabling remote patient care. This allowed remote patient care and reduced hospital congestion.
Another example is Medtronic’s smart insulin pumps, which use IoT to adjust insulin delivery in real time based on glucose readings. This innovation helps diabetes patients maintain stable blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of complications.
3. Logistics
Logistics companies use IoT to track vehicles, optimize routes, and manage inventory, enhancing supply chain transparency, reducing costs, and improving delivery accuracy.
For example, DHL SmartSolutions uses IoT to monitor the condition of assets, particularly in EV battery supply chains. IoT devices track location, temperature, humidity, shock, light, and motion, providing full visibility into goods in transit or storage.
Heineken also leverages IoT monitoring for timely deliveries across 190+ countries. By using real-time monitoring and instant alerts, they quickly detect and resolve issues, even off-hours, preventing disruptions to early-morning deliveries.
4. Smart Cities
IoT-powered smart city solutions are enhancing urban living by reducing congestion, optimizing energy use, and improving infrastructure efficiency. Cities around the world are adopting these technologies to promote sustainability and better resource management.
For example, Singapore’s Smart Streetlights use IoT sensors to adjust streetlight brightness based on pedestrian and vehicle presence, reducing energy consumption by up to 70%.
In Barcelona, a Smart Parking System uses sensors to detect available parking spots and guide drivers in real-time, reducing traffic congestion and emissions.
5. Education and Academia
In education and academia, IoT is used to enhance campus management, improve classroom experiences, and facilitate research in cutting-edge fields like machine learning and cybersecurity.
For example, Stratosphere Lab uses IoT devices to capture real-time data on cyber threats. However, frequent offline issues led to gaps in data collection. With IoT monitoring, the lab improved uptime from 50% to over 94%, ensuring more continuous and reliable data for their cybersecurity research.
Common challenges in IoT monitoring
IoT monitoring faces several common challenges. Let us discuss the top 3:
- Challenge: Data privacy and security issues
IoT devices handle large amounts of sensitive data, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. Weak encryption and authentication can expose your network to unauthorized access and data breaches.
Try these solutions to strengthen security:
- Use strong encryption like Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) and assign unique cryptographic identities to each device.
- Implement Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to manage digital certificates and keys securely.
- Deploy AI-based anomaly detection systems to identify suspicious device activity in real-time.
- Challenge: Scalability
As IoT networks grow, managing more devices, users, and data becomes increasingly complex. Manual configuration is inefficient, and poorly designed data pipelines can create performance bottlenecks.
Try these solutions to scale efficiently:
- Automate tasks like device registration, software updates, and configuration using bootloaders.
- Adopt modular architectures to scale individual components without disrupting the entire system.
- Streamline IoT data pipelines with cloud-based or edge computing solutions for faster processing and reduced latency.
- Challenge: Integration with legacy systems
Many organizations still rely on outdated systems that aren’t built for IoT, making integration difficult. Legacy systems often use old protocols, limiting interoperability and making upgrades costly and time-consuming.
Try these solutions to work with legacy systems:
- Use middleware solutions to bridge the gap between legacy systems and IoT devices for seamless communication.
- Develop APIs to connect legacy systems with IoT platforms without requiring a full system replacement.
- Deploy edge computing nodes to process data locally before integrating it, reducing disruptions and improving efficiency.
Future trends in IoT monitoring
The future of IoT monitoring is set to be shaped by several key trends, including:
- Growth of edge computing
Edge computing is revolutionizing IoT monitoring by processing data closer to the source, offering several benefits:
- Real-time latency reduction: Edge computing has demonstrated a substantial reduction in latency, with studies showing a decrease of 40-60% in time-sensitive applications. In some cases, latency reduction of up to 82% has been achieved.
- By shifting data processing closer to the source, this strategy represents a new form of AWS workload migration, enabling faster response times in critical IoT applications.
This significant improvement enables faster response times for critical IoT applications, such as:
- Autonomous vehicles
- Smart healthcare systems
- Industrial automation
- Traffic management
For instance, in manufacturing, sensors can detect equipment overheating and trigger immediate cooling responses, preventing costly downtimes
- Bandwidth optimization: By processing and filtering data at the edge, only relevant information is sent to centralized platforms, reducing strain on network bandwidth.
- Enhanced predictive maintenance: Edge devices can analyze sensor data from machinery in real-time, predicting equipment failures before they occur.
- AI and machine learning for smarter monitoring
The integration of AI and machine learning with IoT monitoring systems is driving innovation and improving operational capabilities:
- Advanced data analysis: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of real-time data from IoT devices, offering deeper insights and enabling more precise forecasting. For instance, in warehousing, AI can predict demand spikes and optimize inventory management.
- Anomaly detection: Machine learning models can identify unusual patterns in IoT sensor data. This is particularly valuable in industries like oil and gas, where early detection of pipeline anomalies can prevent disasters.
- Automated decision-making: AI-powered IoT systems can make autonomous decisions based on monitored data. In agriculture, for example, AI can analyze soil and weather conditions from IoT sensors to automatically adjust irrigation and fertilization schedules.
- Expansion of 5G networks and their impact on IoT
5G is a big leap forward for smart devices. With the ability to support up to one million connected devices per square kilometer, 5G networks are set to significantly enhance IoT monitoring capabilities.
- Ultra-low latency: With latency times of less than one millisecond, 5G enables near-instantaneous communication between IoT devices. This is crucial for time-critical applications such as autonomous vehicles or remote surgeries.
- Enhanced real-time monitoring: The high-speed, low-latency nature of 5G allows for more sophisticated real-time monitoring applications. For instance, in smart cities, 5G-enabled IoT devices can provide instant updates on traffic conditions, air quality, and energy usage, allowing for immediate adjustments to city systems.
- Improved remote operations: 5G’s capabilities enable more effective remote monitoring and control of assets. In the energy sector, for example, 5G allows for real-time monitoring and control of power grids, improving efficiency and security of supply.
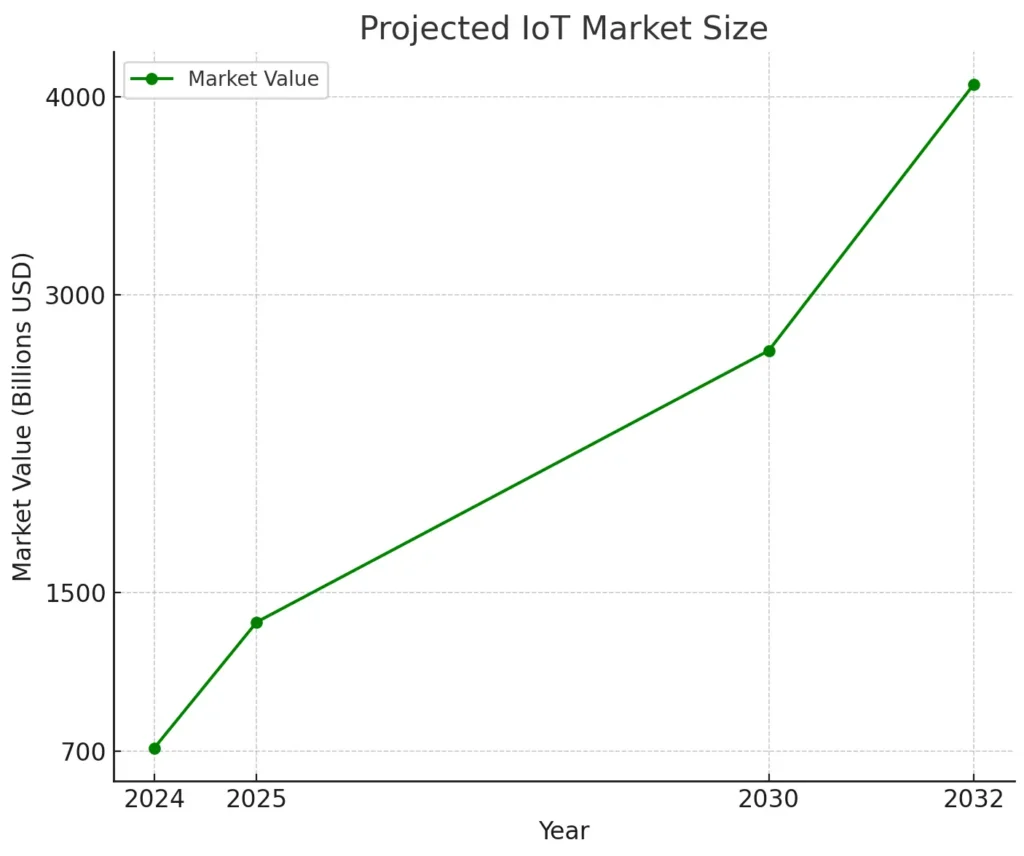
“The global IoT market is projected to expand from $714.48 billion in 2024 to $4,062.34 billion by 2032, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24.3%.” Fortune Business Insights
Best practices for implementing IoT monitoring solutions
Before you start implementing IoT monitoring, keep these best practices in mind to build a successful setup. Following these steps will help you get the most out of IoT while avoiding common issues. Here’s what you need to focus on for the best results.
- Define objectives and KPIs
Before rolling out an IoT monitoring solution, take a step back and analyze your operations. What inefficiencies or pain points are you trying to fix?
Having a clear picture helps you choose the right technology and data strategies that align with your business goals. Setting measurable KPIs ensures you can track progress and continuously optimize.
- Tie your KPIs to business goals, like cutting costs by 15% or boosting efficiency by 20% in a year.
- Use balanced scorecards to track performance and spot trends across different areas.
- Keep refining your KPIs based on real-time data to stay on top of improvements.
- Implement robust data security measures
Security should be a top priority when implementing IoT monitoring. Start by identifying potential risks, including device vulnerabilities, network exposure, and data storage weaknesses. A proactive security strategy helps you prevent breaches, protect sensitive data, and keep your systems running smoothly.
- Encrypt data at rest and in transit using TLS and AES-256 to safeguard against cyber threats.
- Apply a zero-trust model that requires authentication for every device and user.
- Regularly audit and update role-based access controls to limit data exposure.
- Deploy real-time security monitoring tools like SIEM and AI-driven anomaly detection to catch and respond to threats.
- Segment your network to isolate IoT devices from critical business systems and reduce security risks.
- Regular system updates and patches
Keeping your IoT devices up to date is crucial for security and optimal performance. Regular updates address bugs, patch vulnerabilities, and introduce new features to maintain devices’ security and efficiency. A solid update strategy helps prevent disruptions and keeps your systems running smoothly.
- Create a comprehensive firmware and software update plan, including automated update systems for large-scale deployments.
- Use a staged rollout process for updates, testing on a small group of devices before full deployment.
- Leverage edge computing for quicker vulnerability analysis and faster patching to address threats in real time.
- Use AI-driven update systems to prioritize critical security patches based on the latest threat data.
- Have a rollback plan in place to quickly restore systems if an update causes issues.
- Staff training and development
To make the most of your IoT monitoring systems, it’s essential to equip your team with the right skills and knowledge. Well-trained employees will be able to perform preventive maintenance, troubleshoot effectively, and make informed decisions based on the data they collect.
- Develop a comprehensive IoT training program covering device operation, data analysis, and troubleshooting basics.
- Create a mentorship program pairing experienced IoT professionals with newer team members for hands-on knowledge sharing.
- Establish clear SOPs for troubleshooting and responding to system alerts efficiently.
- Set up a continuous learning program with certifications and workshops to keep your team updated on the latest IoT trends and security threats.
- Offer role-specific training tailored to IT security teams, operations staff, and decision-makers to improve overall adoption.
Why IoT monitoring breaks when you treat devices like servers
IoT monitoring fails when teams apply traditional infrastructure assumptions to devices that behave nothing like servers. IoT systems are distributed, unreliable by design, and often offline. Monitoring needs to reflect that reality.
The first difference is connectivity. IoT devices drop in and out constantly. Power cycles, weak networks, and mobility are normal. If monitoring expects always-on connections, alerts become noise. The real signal is unexpected silence, not every disconnect.
Device health also looks different. CPU and memory matter less than battery level, signal strength, sensor output, and last successful check-in. A device can be “up” but useless if it stops reporting valid data. Monitoring needs to validate behavior, not just reachability.
Scale changes everything. Hundreds or thousands of devices generate patterns that single-device monitoring misses. One offline sensor may be fine. Ten percent offline in one region is not. Aggregation and thresholds at the fleet level catch systemic issues earlier.
Firmware and config drift are common failure sources. Devices update slowly, sometimes partially, and not always successfully. Monitoring should surface version mismatches and stalled updates, not assume uniform state across the fleet.
Latency tolerance is another trap. Many IoT workloads are asynchronous. Data arriving late may still be acceptable. Alerting on strict timing without context creates false incidents. Good IoT monitoring uses expected windows instead of exact schedules.
External dependency visibility matters more than usual. IoT devices depend on networks, gateways, brokers, and cloud ingestion pipelines. Failures often happen between the device and the backend. Monitoring only the cloud side misses where data actually drops.
Security signals deserve special handling. Compromised or misbehaving devices may stay online while sending invalid or unexpected data. Monitoring patterns and anomalies helps catch this earlier than simple uptime checks.
The most effective IoT monitoring asks different questions: are devices reporting when expected, is the data sane, and are failures clustered or isolated?
When monitoring reflects how IoT systems actually fail, issues become predictable instead of mysterious.
Conclusion
By the end of 2023, a total of 32 billion IoT and connected devices were deployed worldwide, with projections showing an annual growth rate of 8%, reaching 46 billion IoT devices by the end of 2028. As these IoT networks expand and become even more crucial to business operations, ensuring their security, performance, and reliability is more important than ever.
A robust IoT monitoring system is essential for keeping everything running smoothly and securely. It helps you identify issues early, prevent costly downtime, and protect your devices from potential security threats.
If you haven’t done so already, now is the perfect time to assess your current IoT monitoring system. Explore the tools we’ve discussed to keep your operations secure, efficient, and optimized as your IoT network continues to expand.
Start monitoring with UptimeRobot today. Get 50 monitors with 5-minute checks FREE.
FAQ's
-
IoT monitoring tracks the health, connectivity, and performance of Internet of Things (IoT) devices. It ensures devices are online, sending accurate data, and functioning correctly. Monitoring helps prevent failures in smart devices, industrial equipment, or home automation systems.
-
IoT devices often operate unattended, so failures can go unnoticed until they cause bigger issues. Monitoring helps detect offline devices, network problems, or abnormal behavior early. This reduces downtime, improves reliability, and protects data integrity.
-
Key metrics include device uptime, battery levels, network connectivity, sensor data accuracy, and CPU/memory usage for smart devices. Monitoring may also track firmware versions and alert on outdated or vulnerable software.
-
IoT monitoring focuses on distributed, often resource-constrained devices connected over unreliable networks. Traditional server monitoring tracks central infrastructure with consistent connectivity and resources. IoT monitoring must handle intermittent connectivity and diverse hardware.
-
Alerts often occur when devices go offline, report abnormal sensor readings, exceed thresholds, or encounter firmware failures. Network congestion, power issues, or configuration errors are common root causes.